Malware refers to software designed to intentionally manipulate or interrupt a device’s normal functionality. Examples include viruses, ransomware, worms, spyware, Trojans, and adware. Unfortunately, malware can infect any device with computing capabilities, such as smartphones, PCs, laptops, tablets, and servers.
The first malware to be developed was utterly harmless. However, the advancement of technology, computing, and software development has made malware more prevalent and sophisticated.
Read along to learn how malware works, how it gets into your computer, how to remove malware quickly, and much more.
What is the implication of malware?
Malware is meant to infect devices and networks and harm them or their users. Depending on the type of malware and its goal, malware can appear in different ways. For instance, it can be a low-risk program arriving via ads or something severe impersonating legit software to trick users.
Regardless of the method, all malware types benefit the hacker at the user’s expense and device. Cybercriminals use malware to render computers inoperable, steal passwords, and delete files. It can cause many issues that affect daily operations and the long-term security of users.
Types of malware

There is a wide variety of malware, and new ones appear daily. Here is a list of some of the most common malware types.
- Viruses – These are malicious programs that work by modifying other files in your computer to spread. Different types of viruses exist, but they all spread similarly.
- Spyware – This program enables criminals to access your passwords, keystrokes, and other sensitive information. Note that some spyware types are more perverse than others. For example, those used to monitor loved ones’ devices are less sophisticated than those hackers use to steal bank credentials.
- Ransomware – These are programs that hackers use to encrypt crucial files on the victim’s computer and demand payment to decrypt them. They are also known as ‘crypto-lockers‘. Ransomware can be overwhelming to large organizations, with some of them losing millions in damages.
- Rootkits and bootkits – Rootkits are incredibly advanced as they infect the lowest levels and highly trusted computer code. On the other hand, bootkits affect even lower (or initial) system levels, such as the boot process.
- Bot – Criminals use botnets to control many computers simultaneously remotely. Actually, these botnets are commonly used for distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks on systems and websites. A device is infected with bot malware to join the botnet.
- Adware – This is the least malicious malware type, as it just displays ads on your device. However, don’t disregard adware because sometimes it can be bundled with more sophisticated malware.
- Worms – These malware types can migrate from one machine to another by exploiting security weaknesses. Making it worse, they function on their own without requiring user intervention.
- Trojans – These malicious programs steal personal information, launch an attack, spy on activities, and even crash the device.

How does malware spread?
The spreading mechanism depends on the malware type. Some like worms and viruses are described by the way they spread.
- Worms exploit security flaws in the OS and software to spread without intervention by the user.
- Viruses input their codes in other programs to spread.
- Fileless malware uses inbuilt tools like PowerShell or takes advantage of bugs in software to remain resident without leaving traces on the hard drive.
- Trojan horses trick users to install them by masquerading as a genuine program.
Email is the most common method of distributing malware, although some don’t require human intervention to spread. According to F-Secure, more than 90% of malware infections are caused by malicious or phishing emails.
Mobile device malware usually spreads via infected apps from third-party app stores. However, this doesn’t mean that all the apps on official app stores are entirely safe, so always stay alert.
What is the purpose of malware?

Malware is intended to benefit the creator in one way or the other. Hence, they are involved in severe crimes today.
Each malware type enables the developer to gain power or uniquely make money.
For example, banking Trojans steal crucial data that the attacker uses to drain the victim’s bank account. Some other types are used to blackmail victims, while others are specifically designed for industrial espionage.
Why do cybercriminals use it?
Malware is a broad term that encompasses different types of malicious software, and cyber criminals use them for various reasons, including;
- Stealing crucial information such as credit card data.
- Misleading a victim to provide personal data.
- Taking control of multiple computers to launch botnet attacks against other networks.
- Infecting computers and using their bandwidth to mine cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin.
Signs that your device has malware

These are common signs of knowing your computer has a malware infection.
- Extremely slow performance.
- Uncontrolled redirects or your web browser opens pages you didn’t intend to visit.
- Frequent pop-up ads.
- Infection warning, sometimes accompanied by a solicitation to buy a solution to the issue.
- Problems with starting or shutting your computer.
The presence of multiple signs indicates that your computer has a malware infection. For example, many pop-up ads and browser redirects are vital pointers that your computer is compromised.
How do I detect malware?
While some malware types are less subtle, others don’t even leave a trace, making it difficult to locate them.
However, some others, like adware, are simple to detect because you start to receive abnormal pop-up ads.
Adware attacks are different from ‘malvertising’ – another malicious technique involving ads. In case of adware, the malicious program is responsible to show ads. That’s how it benefits the attacker. However, malvertising includes exploiting ads to deliver malicious files onto the target devices, which may include spyware, viruses, trojans, or even ransomware.
Also, ransomware is distinguishable because you will receive a ransom message.
Otherwise, the other way to detect malware is when your computer starts to behave unusually.
Installing an antivirus application can defend your computer against most malware types with reasonable accuracy. It is good to heed the antivirus’s warning if it detects malware. With reliable software like TotalAV, false positives are less likely.
How do I remove malware?
You need to do specific things if you suspect a malware infection. While the aim is always the same — getting rid of the malware — the process to achieve this goal may be different according to your respective device.
So, below we explain the malware removal steps for devices running different operating systems.
Remove malware on macOS and Windows

For desktop computers and laptops running on Windows or macOS, here’s how you can clean your devices.
1. Stop the internet connection
First, you should discontinue the internet connection. It is even better to deactivate the home router because some malware can resist shutting off.
Furthermore, others may be siphoning your data from your device to a hacker’s server without you knowing. However, disconnecting the internet connection breaks this main link. If you also disable the router connection, you will go completely off-grid.
2. Activate the safe mode
If you have suffered a ransomware attack, enable the safe mode on your system to launch the core functionalities. That is why you see separate partitions for system files when installing Windows 10. Here is how to activate the mode:
- On Windows, press Ctrl + F8 during boot up. Then, choose Safe mode with networking out of the list of options.
- Restart your macOS system, then press and hold the shift key before the Apple logo shows up. Once you enter your password, you will access the system in a safe mode.
Booting in the safe mode ensures that the malware does not compromise the essential system files, making it easy to clean up. System wipe may be the best solution if you cannot access your system’s safe mode.
3. Scan for malware
Install an antivirus application and run a full scan on your computer. A reliable service should identify and resolve the threats. Moreover, it is always good to keep the antivirus active to get real-time protection.
4. Re-install or change the browser
Some malware types compromise your browser’s default homepage to infect your system when establishing an internet connection. The best solution is to wipe off all the saved settings and cache in your browser before uninstalling it. Then, use another browser or reinstall the previous one after confirming that you’ve eliminated the malware.
5. Check whether your device is malware-free
Finally, start your computer and initiate the normal mode. The best way to know if the malware has gone is by running a malware scan with a reputable antivirus.
6. Computer wipe
Another effective way to remove malware is by wiping your computer. Use the following steps to do it.
- Create an install drive on a clean computer. This is an easy process for Windows as you will only need to download the ISO file and create a bootable flash drive with Microsoft tools. If you are using macOS, use the Internet recovery instead of the regular model.
- Back up your data. Some files might be infected, so don’t open them on a clean computer.
- Boot from the internet recovery or USB drive and install the OS to your computer’s internal hard drive. This will enable you to overwrite your data.
- Boot your machine from the internal drive and proceed with the setup process. Once you finish it, your computer will feel brand-new.
- Finally, install an antivirus program, connect the backup drive, and scan files. Don’t open the computer until you confirm the backup is clean.
Remove malware from Android and iOS

Removing malware from iOS and Android devices (smartphones, tablets, and others) is slightly different from doing it on your computer.
On iPhone
The best way to clean your iPhone or iPad from any malicious programs is to scan via an effective antivirus solution for iOS.
However, finding one may be difficult due to Apple’s iPhone security features. During scans, an antivirus program requires unrestricted access to the operating system’s internal functions, which Apple doesn’t support.
So, in that case, below are some measures you can take to eliminate viruses and other malicious files from your iPhone.
- Reboot your phone. You can remove some non-persistent viruses from your iPhone with a simple reboot.
- Connect to another network. One way to solve network-related issues is by connecting to another network or using LTE rather than a WiFi connection. This will help to prevent ads on HTTP sites and additional pop-ups. Try more drastic measures if this is not a suitable solution.
- Add 2FA and change your iCloud password. Adding two-factor authentication and changing your iCloud password will thwart account takeover. Also, remember to disconnect unrecognized devices from your Apple ID.
- Wipe your iPhone completely. If the above tips do not work, wiping your phone may be the ultimate solution. It should remove all the traces of malicious programs and files.
On Android
Android functions a little bit differently from iOS devices. For instance, apps can freely access the operating system. Hence, running antivirus software on Android can be more effective than iOS. However, a virus infection will do more harm. The tips below will help you eliminate a virus from your device.
- Uninstall unrecognized apps. They are most likely the cause of the malware problem on your device.
- Change the connection method or use a different network. Maybe the malware-like symptoms the network causes your computer exhibits. Connecting to a different network can help stop pop-up problems and other similar issues. Alternatively, switching between mobile data and Wi-Fi can be a remedy to your problem.
- Add two-factor authentication and change your Google account.
- Use strong passwords on your accounts to prevent possible takeovers.
- Wipe off your Android device.
Completely wiping off your phone can solve different malware types, although you should take it as a last resort.
Effective ways to safeguard against malware

Currently, thousands of internet security solutions promise protection against malware. However, remember that all antivirus solutions are not the same. For example, some concentrate on extra features while others emphasize performance and speed.
Both Windows and macOS come with antivirus software. Windows uses Microsoft Defender, and macOS employs various security features such as Gatekeeper and Xprotect. However, these options only provide basic protection and don’t suffice to handle today’s threats.
- Choose antivirus software with real-time protection to protect you around the clock in the background.
- It should be a reputable provider. Some malware masquerades as antivirus programs, so be careful with the option you choose.
Moreover, your mobile phone or tablet can be infected with malware. In this case, always install apps from official app stores, like Google Play Store and Apple App Store. Also, ensure your phone’s system is up-to-date to prevent malware that takes advantage of security vulnerabilities.
History of malware
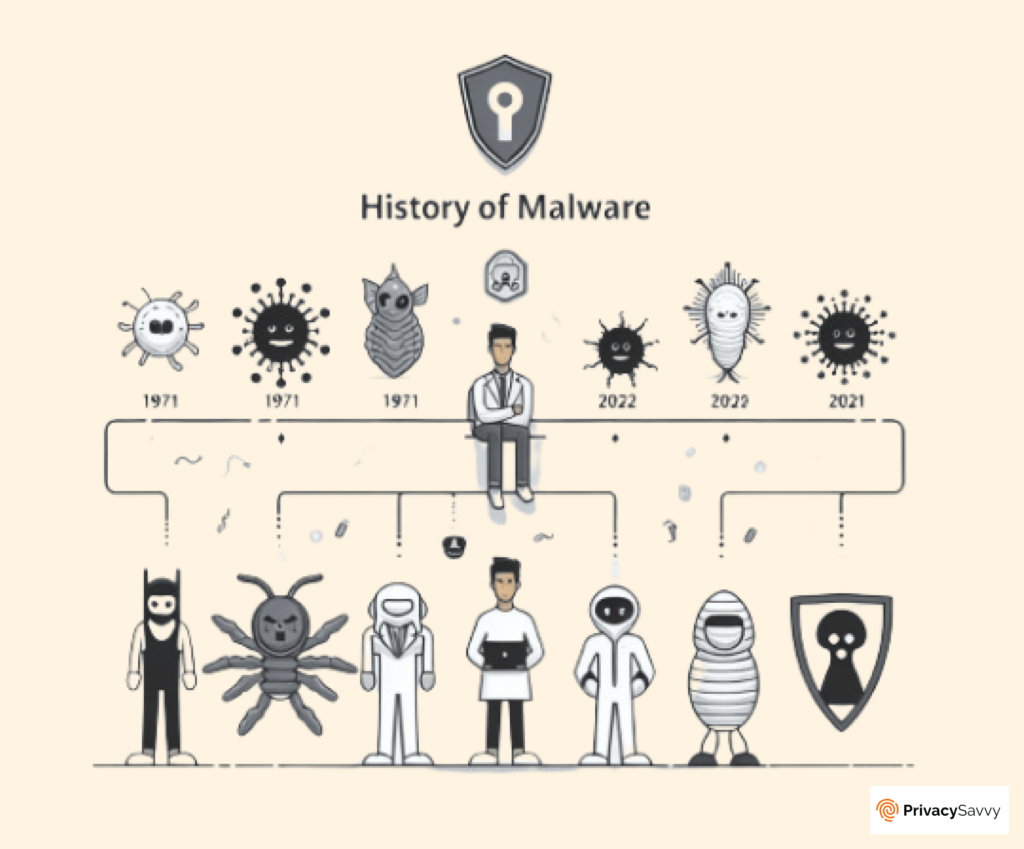
Initially, the malware was harmless and couldn’t harm the computer. The first malware, “Creeper” (technically, a ‘worm’), was created by Bob Thomas in 1971 as an experimental computer program. It could only spread through local connections without causing any damage.
Another prominent example, “Elk Cloner” (technically, the world’s first ‘virus’), was created by a 15-year-old Richard Skrenta around 1982. The virus could affect Apple II computers via floppy disks. Also, it was harmless and only displayed a short poem.
However, an MS-DOS virus, known as “Vienna,” discovered in 1998, was a game-changer. It was more malicious than the previous versions, as it could corrupt files. Other viruses that started to appear at that time include Cascade and Lehigh.
However, perhaps the most dangerous malware at the time was AID Trojan ransomware. It paved the way for other more severe threats like WannaCry and Petya.
Here are some of the notable examples that started to appear since then:
- The Michelangelo Virus in 1992 – a malware that infected hard drives.
- Melissa in 1999 – an email-based virus used to send infected files.
- ILOVEYOU in 2000 – could download a Trojan and infect over 10 million Windows computers.
- WannaCry in 2012 – encrypted Windows computers worldwide and demanded ransom in bitcoin.
Unfortunately, different malware types are evolving and becoming a big menace. However, you can stay safe from these threats by practicing cyber hygiene and installing a reliable antivirus program.
Final word
With ever-growing types of malware today, it’s becoming harder and harder to know, avoid, and remove them all. In addition to following all the malware prevention guidance covered in this article, you should start using reliable cybersecurity tools.
Although antivirus software is a great solution, you can go beyond simple file scanning to improve your security.
Many corporate endpoints and security suites scan websites, email attachments, and other common mediums of attack. For example, Outlook and Gmail scan attachments by default.
It is crucial to prepare for the potential effects and protect against malware. For instance, ransomware affects files, so backing up your data can be helpful.
In addition, you should incorporate multi-factor authentication. It will prevent credential-stealing spyware from accessing your accounts without approval from a second factor.
Nonetheless, common sense and vigilance matter regardless of the technique or software you choose to use. As mentioned earlier, some antivirus programs are not genuine, so don’t trust them blindly.
FAQs
Malware is a broad term for all types of malicious software. Conversely, a virus is a kind of malware that inserts malicious code into other programs and self-replicates itself.
Yes, some malware types can cause your computer to function slowly, making it downright useless.
Hackers develop malware for various reasons, including theft, blackmail, spying, and pranking.
In general, macOS is considered more resilient to malware than Windows. However, nowadays, hackers create malware specifically for macOS, so take safety precautions.
It can spread into your system, crack weak passwords, and spread through networks. Other malware types can redirect you to malicious websites, spam you with ads, and lock up crucial files. Malware infection can also result in data theft or even damage to the entire system or device.
There are different ways your computer can get a malware infection. For example, you can browse through a hacked website, download infected files, view genuine sites serving malicious ads, or open a malicious email.





