On the one hand, the internet has facilitated us in all walks of life. On the other hand, it has also risked our personal privacy and online security. (Well, that’s how it works! We really can’t help it.)
However, it doesn’t mean that anyone connected to the internet has been breached. It’s just about the vulnerability and the potential exposure of innocent users to cyber threats that one should be wary of.
In this detailed and ultimate guide to internet and computer security, we’ll highlight the basic digital privacy tips for you.

A quick look at what’s there in this security guide
- Understanding the internet
- Develop a mindset to implement basic security tips
- Surf safely
Understanding the internet

Creating a key to open a padlock needs you to understand how it works. That’s what it takes to make and use the right key for it.
Likewise, to protect yourself on the internet, you should first understand how things work in the online world. Only then would you be able to work out a viable internet and computer security guide.
Basically, the internet is all about your interaction with third parties. In fact, this is how it’s built – by letting you network with people in other parts of the world.
By this, we don’t literally mean you conversing with your kith and kin in other cities/countries. Rather the services you use, particularly the ones that you do not own, constitute the internet, where the latter serves as a medium that links your device with the services, such as Google.
This linkage develops over the network data or the traffic generated from your device when you request access to it via the service website link or the URL. The internet transmits it to the destination (a third-party, like Google). This destination is the ‘server’ – the dedicated computer – belonging to the destination third party.
Once the data reaches the destination website server, it processes your request and responds accordingly. That’s how it appears on your computer screen.
For example, if you’re asking to sign in to a service, you’ll then see the login page load on your device browser.
After you type your login credentials (username/email address and password) and press ‘Enter,’ the credentials then travel across the internet to reach the website’s servers. The latter match your credentials with the ones in its database to authenticate your sign-in request. After validation, it then lets you sign in, and you eventually enter your online account.
This basic procedure applies to almost all websites and apps, including email services, social media apps, or even your online banking site. That is, your data travels over the internet to the destination servers, and the server processes and validates your request and responds accordingly.
Besides, thanks to the convenient office software and other such programs, you also send documents and other media files digitally. So, this kind of data that you often share as ‘attachments’ to others also becomes a part of the data you send online.
Moreover, to interact with other human users, such as your family, friends, or colleagues, your data transmits all the way from your device to the respective website’s servers and then to your target recipient’s computer(s).
Throughout this process, the data remains vulnerable to cyber-attacks. An adversary can either hack the target servers to steal your data or your own device or can intercept the data in transit.
That’s what computer internet security is all about. You need to protect your data not only at your device level. Rather you should also do your best to keep it safe during transit as well as when it reaches the destination server.
How to prevent hacking and cyber threats

As you now know, the internet isn’t a single entity that you could put under lock and key for security. Instead, it’s a network of many different components.
And when you take a look at one-to-one communications like email, social media, or messaging apps, things expand further and get even more complicated as more hardware and software get involved. At the same time, the probability of your data being intercepted, spied on — or even stolen increases.
Sounds overwhelming? Don’t worry!
However, things look scary given the increasing incidences of cyberattacks and a complicated internet world. However, protecting yourself from more cyber threats isn’t difficult.
In fact, most cyberattacks succeed only because of people’s negligent attitude toward basic computer security.
So, if you wish to stay secure, you don’t have to search for a voluminous cybersecurity guide. Rather you just have to focus on the areas that you interact with while you’re online. That often includes the things we listed at the beginning of this section.
Those are the key areas that you should understand. Those are the components that can expose or protect you against cyber threats.
The moment you connect your device to the internet and start browsing, ask yourself the following,
- Am I connecting to the right website?
- Is my data safely transmitted to the website?
- Does the target website have secure servers?
- If the site gets hacked, what will happen to my data?
- Am I really chatting with Bob – my old school friend – or an impersonation of him on Messenger?
- Is someone seeing or reading my messages to family and friends?
- Has my email reached my boss safely?
- Did my bank really send that weird email to me?
- Am I lucky enough to win a $100 million lottery?
- Why can’t I remember my distant grandma who just left me all her property worth million dollars?
- What is that strange icon on my smartphone? When did I install that app?
- Why is my computer working automatically? Is it really that smart?
Steer clear of unsafe places
It’s not a driving tip for your car or bike. Rather the basic tip to stay safe from mishaps on your online journey.
As we explained above, when you go online, you must ensure that your data safely transmits to the destination websites. That’s because hackers are all around you in the virtual world. And the easiest way for them to steal your information is to intercept your data either during transit or at the destination. So, you have to steer clear of them.
This is only possible when you opt for safe websites. If you accidentally come across an unknown/unfamiliar website, make sure to stay away from it.
So how can I check if a website is unsafe? How to identify the safe ones? I hear you ask!
Below, we explain it all.
Check for HTTPS Websites
The moment you open your browser and connect to any website, you’ll see a padlock sign before the URL (the website link) in the address bar. Regardless of the browser you use, this padlock indicator will always be there with minor changes in its appearance.
For example, let’s take a look at how this website’s URL appears when you visit it through Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome, or Microsoft Edge.
Likewise, if you scroll above to see the URL of this article, you’ll see the same padlock sign.
So, what is it?
This is the basic indicator of a site’s security. This indicator represents ‘HTTPS communication. It shows that the communication between your device and the respective website is secured with encryption.
HTTPS or HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure is basically the secured predecessor of the previous HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol). However, it is different and secure in that it applies SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) that encrypts the data during transit, back-and-forth.
It means that what the online world outside the secure SSL tunnel sees is that you have established a connection to a website. Besides that, all the other data that you input, such as your passwords, contact numbers, credit card details, etc., remain protected from snooping and tampering.
So, the first thing when you start your online journey is to only visit those websites that respect your security and apply HTTPS (like PrivacySavvy).
You can clearly verify the HTTPS status by checking the padlock sign. If this sign doesn’t appear or appears as broken or crossed, then it indicates that the website either lacks proper HTTPS implementation or has no HTTPS at all. It’s better that you avoid visiting such sites since your data (such as passwords) will be visible to the online world.
Nonetheless, don’t take this padlock sign as a security label. Despite applying HTTPS, the site may have other malicious components, including malware as well. So, make sure that you know and trust the website you visit.
Pay attention to what your browser considers unsafe

As the online world is being flooded with scam websites, browsers have begun showing warnings whenever a visitor comes across such a site.
Whether you use Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox, or any other site, you may often come across such warnings labelled “Deceptive site ahead” or something like that. These warnings basically appear when your browser detects the website you’re trying to visit as potentially unsafe.
Basically, these warnings are primarily powered by the Googlebot of the Google search engine. (We’re naming this one since it is the most popular search engine.) This Googlebot crawls every site indexed with the search engine and scans its code while searching for content. Whenever it detects any malicious code, it labels that site as unsafe. Then, it adds the website to a detailed list of bad websites.
This list is what empowers the Safe Browsing feature of most browsers, including Apple Safari and Mozilla Firefox. When you attempt to visit any website, the browser matches your query with the list of bad websites. And, if it detects a malicious web link, it displays a warning to you.
These warnings may also appear if a previously safe website gets hacked. So, don’t be annoyed if your browser blocks you from visiting a website that you previously visited easily. Rather it’s better to wait for the matter to resolve. Meanwhile, you can visit another similar website.
The privacy-savvy users may sense some kind of tracking here. If you’re one of them, then you’re certainly right. But that’s how the safe browsing feature works. If you wonder how to make your browsing experience private, you may consider using private search engines and private browsers that minimize data collection from your browsing habits.
Moreover, you can apply other strategies to prevent browser fingerprinting and encrypt your online traffic to stay protected from online tracking entities.
Be wary of dubious URLs and attachments
If you have limited browsing habits, you’ll seldom visit an unsafe web link. Perhaps, it’ll only happen if one of the sites you frequently visit gets hacked.
However, there is another way through which you’ll most often fall for malicious links – phishing.
In simple words, phishing is the way through which scammers and hacking bluff you into clicking on malicious links. It can happen through any means of communication, such as text messages, emails, messages on social media, or even phone calls.
But the most common means of executing phishing scams is via emails. These emails mimic otherwise legit senders, such as your bank or social media service. The message body includes malicious links embedded in apparently harmless texts, such as “click here”, or “get now” buttons. Once you click on the link, you’ll be redirected to the phishing web page that either asks you to enter your data or downloads malware to your device. Either way, the attackers can gain access to your information, which they can use for any malicious purpose.
The same applies to the attachments as well, like document files, PDF files, image files, GIFs, audio, or even videos. Tapping on or downloading the attachment can install malware on your device that could further assist the hackers in tracking you.
Besides tracking, the attackers can also target you for ransomware attacks via the same means.
Therefore, before you open any message, make sure you trust the sender and know the reason for the message. Winning a lottery or receiving property worth millions from a distant aunt is too good to be true. Likewise, if you keep an eye on your credit card transactions, there’s no reason for your bank to block your credit card or other payments.
Similarly, if you think your Facebook account just endured a hack, don’t click on any links given in the emails or messages. Instead, head on to Facebook and check your account yourself.
In short, if you find any incoming message, either via text or email, unsolicited, it’s better to ignore it. Or if in doubt, you can reach out to the apparent sender via some other means to counter-check the authenticity of the message.
Check for a website privacy policy
A website needs to have a transparent privacy policy that outlines user data collection, usage, and protection. This is a legal requirement in many countries, including the EU, Canada, and Australia, where data privacy laws have become increasingly stringent. By having a privacy policy, website owners demonstrate their commitment to complying with these regulations and safeguarding their users’ privacy. Before providing personal information, it is advisable to locate and carefully review a website’s privacy policy.
Find their contact information
A website’s trustworthiness is enhanced by the presence of its contact information. In fact, a survey revealed that 44% of respondents would leave a site that doesn’t include a phone number or other means of contact. A secure and reliable website should prominently display contact information, such as email address, phone number, physical address (if applicable), a return policy (if applicable), and links to their social media accounts. Although these details do not necessarily guarantee protection, they signify the possibility of contacting someone for assistance.
Verify their trust seal
If you come across an icon on a website that says ‘Secure’ or ‘Verified’, it’s likely to be a trust seal. Such seals indicate that the website has partnered with a security company. Trust seals are typically associated with HTTPS security, but they can also signify other safety measures, such as the last date the site underwent a malware scan. Despite 79% of online shoppers expecting to see a trust seal, relying solely on its presence is insufficient. So, it’s equally crucial to verify the authenticity of the badge. Fortunately, this can be done easily by clicking on the badge and checking if it leads to a verification page, confirming that the website is working with the specified security company. It’s also advisable to conduct your own research on the company that provides the trust seal.
Ensuring password security

Just like you protect the keys of your home’s security locks, you need to protect your passwords in the online world. It’s like your digital key to enter various services, which, if stolen, will be dangerous for you.
That’s why it’s always advised not to share your passwords with anyone, even with your friends. Or if, at all, it becomes necessary, avoid sharing it via common means of communication like a text message, email, or other.
It’s the importance of your password that the hackers keep trying to steal it. If known, they can seamlessly sign in to any service you use, impersonating themselves as you.
While things sound easy until this point, unfortunately, the hackers today know that you won’t likely share your password so easily. That’s why they keep trying various tricks like phishing to steal your credentials.
Besides, they also try other strategies like password guessing or brute force to simply guess your password without even asking you. It’s a more dangerous thing as you won’t even get a hint of when a perpetrator cracked your password.
At this point, password security becomes a worth-discussing topic.
Let’s take a look at what you can do to secure your passwords from such malicious attacks.
Create strong passwords
The harder your key is to duplicate or break, the safer you are. The same goes for passwords. Stronger passwords take more time for a stranger to guess. However, to make sure that something is difficult to crack for a hacker, it should be as weird for you to remember too.
For example, things like your pet’s name, your school, or a variant of your name are too easy to guess.
In fact, given the huge number of internet users today, you will likely unknowingly share your password with someone else you don’t know.
If you’re skeptical about how this is possible, take a look at our detailed guide, where we have discussed the most hacked (and the worst) passwords. You’ll be amazed to see how millions of users have set up the same password globally.
This commonness of passwords is exactly the thing that makes hacking easier for the perpetrators.
So, what you should do is set up strange passwords. Consider making it long with an alphanumeric+symbols combination. This will make them difficult to be guessed or brute-forced.
To learn this thing in detail, take a look at our detailed guide to creating strong passwords.
Avoid reusing passwords
Even after you create a strong password, it’ll be of no good if you keep using it across all your accounts.
Although, it’s easy to reuse passwords on other sites. At least you save yourself from remembering tens of awkward strings that serve as your passwords.
But this is the basic thing to avoid, as recommended by every genuine computer security guide you’ll ever read. That’s because if in case, one of your accounts gets hacked or the password gets breached, you put all your accounts the risk of hacking.
We won’t delve into much detail here. Perhaps, you can go through this extensive guide on password reuse dangers if you’re eager to know how exactly this habit constitutes a bad internet security practice.
What we want to emphasize here is that you must ensure not to use the password on multiple accounts. Ideally, you should memorize all your passwords by heart (if your kids can memorize their lesson, you should also memorize your passwords too.)
However, if you’re bad at remembering things or are too stuck to focus on this thing, you can try going the traditional way to maintain diaries. You can maintain a password diary where you can note your login credentials.
This strategy will still likely benefit you in any unfortunate incidents of theft at your home. The robbers would hardly think of you as writing down passwords. They’ll instead focus on other assets more.
However, this isn’t entirely a foolproof idea. If the thief turns out to be a tech freak, he might be lured toward your password diary too. Besides, your family and colleagues would always love to get their hands on this worthy diary to know what you do online.
So, what else would suit you the best? Use a password manager
Use password managers
In simple words, a password manager is a wonderful tool for managing all your passwords. They’re like a digital diary for you where you can store the login credentials for all your accounts. In turn, you can lock these tools with a password that only you would know.
In this way, this useful software saves you from the hassle of memorizing a huge list of passwords. Rather, all you need to remember is just one password to sign in to your password manager and access all your passwords.
Today, these password managers have evolved to serve you more. Precisely, they now not only store your passwords, rather, but also let you store any or all of your important data with them. This even includes your passport number, IDs, bank account details, and credit card numbers.
Besides storage, these password managers also help you create strong and unique passwords. They also automatically input the passwords as required in any online form, thus saving you time and effort.
Also, they alert you whenever they detect a breach of any password so that you may consider changing that.
If you wonder where to find such a useful resource, then check out this list of the best password managers.
Apply two-factor authentication
Regardless of how strong a password you set up, it’s always vulnerable to hacking and brute force. Or maybe, your password manager might suffer a security breach that could expose your passwords.
It means that you need to protect your account security via some other method.
How about adding a double-check on sign-in attempts?
That’s where two-factor authentication comes in. While our detailed guide elaborates well on two-factor authentication, here we give a quick overview.
Two-factor authentication (2FA), or multi-factor authentication (MFA) is all about adding another security layer to your account. So, even if someone knows your password and tries to sign in to your account, 2FA or MFA will block such attempts.
It is because this method involves the authentication of a login attempt via a source other than your password. In most cases, this is achieved by sending a verification code to your email or phone number. You should then enter this code after your password while signing in to your account.
Alternatively, 2FA can be done via an authenticator app or by biometric scans like your fingerprint or iris scan.
Sending a numeric code to your mobile phone number via text message (SMS).
This is the most prevalent type of two-factor authentication (2FA) because of its ease of implementation for service providers and the ubiquitous nature of mobile phones.
To activate this method, you must furnish the website with your mobile phone number, where you’ll receive a test code on your phone as a security measure. Once you enter the verification code on the website, 2FA will be activated on your account.
Subsequently, whenever you attempt to log in, the website will dispatch a unique code to your mobile phone, which you will have to enter to gain access.
Using an application on your phone to generate codes
Several applications, including LastPass Authenticator, Authy, and Google Authenticator can generate 2FA codes. If you are visiting a website that supports any of these apps, the instructions for setting them up will be provided on the login settings page or security page.
Typically, you are supposed to download an authentication app from the Play Store and scan a code from your website with your camera. This will create a designated “slot” for that website in your authenticator app, displaying a dynamically changing numeric code. Once you enter the current code into the website, 2FA will be activated on your account. Whenever you log in, you must launch the app on your device and enter the code displayed for that specific site at that time.
Advantages and disadvantages of both types of 2FA
When it comes to two-factor authentication (2FA), using the SMS method can be easier because it doesn’t require installing an app. Instead, you receive the login code via text message. However, the downside is that you need mobile network coverage to receive the code. If you’re in an area with poor coverage, you won’t be able to receive the code. Additionally, if you frequently travel and change your phone’s SIM card, your phone number will change, so you may not receive the code.
Alternatively, using the app method means you don’t need mobile network coverage to receive the code. The app generates the codes on your phone, so you can still receive a login code even if your phone has poor network coverage. However, transferring the authentication app to another phone can be more challenging. Typically, you’ll need to disable 2FA on all of your accounts, install the app on the new phone, and re-enable 2FA.
Dealing with malware attacks

Perhaps, this is what you were looking for in this detailed computer protection tutorial, weren’t you?
For those who are still familiar with the term “computer virus” but don’t know much about “malware”, let us explain that both are the same.
Basically, the term seamlessly replaced the older word “virus” because, today, malware isn’t confined to viruses only. In fact, viruses merely constitute a type of malware.
Malware is an umbrella term that includes all sorts of malicious computer scripts, from small codes to full-fledged programs. The other common malware types that you might have heard of include spyware, adware, ransomware, trojans, keyloggers, crypto miners, and more.
So, you see, your online security doesn’t remain vulnerable to viruses only. Rather you have a lot more threats to deal with.
Don’t panic; we’ve got you covered in this security guide.
How to detect a malware infection
Before you learn how to protect your computer from viruses, you should know how to know when your machine actually gets infected.
Basically, detecting an issue (precisely, malware) is often difficult. That’s because most malware possesses stealthy capabilities. In other words, they hide their presence on your device by evading or disabling your device’s security mechanisms.
Hence, they sneakily persist and establish themselves in the background while repelling all countermeasures. Once done, they then begin executing the intended malicious activities.
Before, during, and after the malware infection, you may likely not see the malware itself. However, if you closely observe your device, you may notice something is wrong.
For example, if your laptop or computer gets infected, you’ll observe excessive consumption of resources, particularly the hard drive, and power. As a result, you’ll find your computer performing terribly slowly. Some malware, like crypto-miners, can cause excessively high consumption creating a denial-of-service state (like system hang or crash).
Likewise, you’ll notice excessive heating of your computer and loud noise, even when you’re not using it aggressively. Sometimes, you may also see your hard drive indicator blinking quickly without specific activity from your end. This also shows that a program is running in the background.
In the case of your smartphone, you’ll perhaps find it transformed into a ghost phone. Besides overheating and sluggish performance, you may also notice weird sounds from the device, such as alerts or beeps, even when not in use, camera light turned on without prompt, and excessive appearance of ads.
In short, if you spot anything weird or unusual on your device, it’s time to scan it for malware infection.
A web browser infected with a virus may display abnormal behavior, such as adding new bookmarks, extensions, or homepage changes, without your consent, indicating a possible malware attack.
Computers usually give notifications before automatically restarting after an update. However, if sudden and repetitive, it may indicate a malware attack, requiring assistance from a system administrator or IT specialist.
Malware may display error messages to trick users into granting more system permissions or downloads. So, you should be wary of any unfamiliar or suspicious error messages, especially those that appear slightly different from typical computer error messages. If you receive a recurring, unidentifiable message, you should search for the exact wording of the message online and have your device checked for malware if necessary.
Some malware has self-defense mechanisms that can disable antivirus programs to avoid being removed, but reliable antivirus software should alert users of such attempts. If an unprompted warning appears, you should be worried, as it could be a sign of a malware attack, especially if it occurs after recently activating the software.
In addition to disguising itself as harmless, some malware can install a program on your device that appears legitimate, with a name and icon that look innocuous. Therefore, you should consider any program or application suspicious if you are unfamiliar with them or don’t remember downloading them. Ransomware and other types of malware can restrict your access to your system or specific files until a ransom is paid. Usually, ransomware attacks will make it clear that payment is required for a decryption key. Still, even without a ransom note, the sudden inability to log in to your computer should be taken as a warning sign of a potential malware attack.
Malware detected – what next?

The Internet has become a key part of our daily lives, revolutionizing how we communicate, work, shop, learn, and socialize.
However, as our dependence on the internet increases, we become more vulnerable to malicious threats, including phishing attacks, worms, spyware, rogue ware, adware, bots, and Trojan horses which target Internet users daily.
Internet users can implement various security measures to reduce their risk of being attacked. Victims of crimeware attacks can take these steps to respond to the incident.
- Disconnect: If you experience a crimeware attack, disconnect from the Internet immediately to stop data transmission. Disable the network connection on your device by following the steps in the settings menu. Contact your IT department if the attack occurs at work or your Internet Service Provider for personal devices.
- Scan your device: To prepare for such incidents, it’s important to have up-to-date antivirus software installed. These programs can detect and remove crimeware threats from your device, so it’s important to run periodic scans and set up automated scans. However, the software may sometimes detect the threat but cannot remove it.
- Create backup: You should backup your files and folders regularly to protect against potential data loss during the recovery process after a crimeware attack. In fact, you can use backup software for this purpose or another hard drive or removable drives such as a flash drive, CD, or DVD.
- Monitor your online behavior: Stay cautious and mindful of what you click on while browsing the Internet. Steer clear of questionable websites and ads, and keep in mind that if something appears unusual or appears too appealing, it most likely is a cause for concern.
- Reinstall your operating system: Reinstalling the operating system may be necessary to eradicate the threat. This is especially for more sophisticated malware that can hide deep in the system using rootkit techniques, making it undetectable by antivirus software.
In case of online fraud, take these steps:
- Close all accounts: If you’re a victim of online fraud or identity theft, close all affected accounts immediately before the thief has time to access them. Contact the financial institution to discuss the impact and the necessary steps to take.
- Set up fraud alerts: Setting up a fraud alert with TransUnion, Experian, and Equifax is important to control the damage an identity thief can do to your stolen information. It is a crucial step to prevent creditors from allowing any changes or new accounts before contacting you.
- Keep an eye on your credit reports: Fraudulent activity may take some time to appear on the reports, so some agencies offer quick turn-around reports or alerting services for an additional fee. This might be necessary depending on the level of threat and potential impact.
- Use strong passwords: There are many tricks to create formidable passwords. The most common is using numbers, symbols, and words and changing them regularly.
Note:
Windows users often need to install another antimalware program on top of Windows Defender. However, you should never run two antimalware programs on the same device. It’s because they will counter each other’s actions and will also burden your device. If you really need to install another antivirus in the presence of the first one, better deactivate or disable the previous program.
Learn system backup and restore
Although, you can fend off a malware attack in the way we just explained in this security guide. But, what about the data loss you might suffer?
Often, malware attacks are not as dangerous from this aspect (this is what they pose) But, in the background, they might leave traces even after an anti-malware scan. Those backdoors and other components that previously acted safe may be left on your system.
It’s because their apparently non-malicious activity might not trigger the antimalware to take action. However, those leftover traces may facilitate a subsequent malware infection on your device.
Besides, in case of a ransomware attack, the damage is done directly to your system data. So, even after you have involved cybersecurity professionals in cleaning your system, you might not find it working the same way as it did before.
Does it mean you’re left helpless?
Not really, if you are always prepared to deal with hackers and viruses. That’s where system backup and to restore come into action.
(System restore is not the same as backup restore, which generally refers to restoring backed-up data. We’ll talk about it in detail in later sections.)
System restore is a built-in utility in your computer that lets you roll back your system status to a previous state. This feature lets you retrieve deleted files or restore previous configurations in case you aren’t comfortable with the current settings.
The same utility can help you restore your system following a malware infection. After you remove the malware from your device, you can then revert your system to a pre-infection state.
Here’s how to use system restore on different devices.
For Windows:
Go to the Control Panel > System and Security > System > Advanced system settings > System Protection > System Restore.
Then you can select a previous restore point on your device.
If, however, you see the “System Restore” button unclickable, then you need to configure this setting first.
For this, you have to select a drive and click on the “Configure” button. Then select the option “Turn on system protection”, allot a drive space for storing restore points, and click “OK.”
Once done, your device will start creating restore points which you can revert at a later stage when necessary.
For macOS:
On your Macbook, you will find the system restore settings under the macOS Utilities menu. Here’s how to reach the option.
Restart your system. Then immediately press and hold the Apple key+R button. You will now see the system restore options on the screen. Click on the “Restore From Time Machine Backup” to restore your device to a previous state.
Alternatively, if you have backup all your important data elsewhere, you can choose the “Reinstall macOS” option to wipe everything on your device (including any malware or its traces) and reinstall the system.
For Linux:
For now, Linux distributions do not have any native backup or system restore option.
However, you can opt for third-party backup apps to handle the task for you, such as Jungle Disk or CrashPlan.
Ensuring safety when using public WiFi

Public WiFis are very attractive for all internet users, especially today when spending even a second without the internet is difficult.
However, you need to understand that public WiFis aren’t that good at all. In fact, they’re more dangerous for your online security. Because of their open, free-to-everyone availability, and the subsequent attraction of users to these hotspots, public WiFis serve as a harbour to criminal hackers.
In fact, in certain situations, the hackers even set up fake WiFi networks at such places just to bluff you. At times, you can’t even distinguish fake WiFi from legit free WiFi at a place.
The hackers wait for you to connect to these WiFis. They then steal all your data transmitted over the network, including sensitive details like your passwords and banking data.
Therefore, you need to remain cautious while using public WiFi.
First, we strongly advise you to avoid using such free Wi-Fi. You can instead use your mobile data to stay online wherever you go. It’s a costly approach, but it’s still better to spend a few bucks than compromise your personal security.
But if you really need to use public WiFi at any time, does it mean you should compromise your privacy?
Definitely, no!
Well, we have already covered this thing in detail in our comprehensive guide on using public WiFi.
But, as a quick recommendation, here’s what you should do.
Use a VPN
The key to using public WiFi securely is first connecting to a virtual private network or a VPN.
Wondering what it has to do with WiFi?
Well, as you already know, a VPN encrypts all your data before it reaches the online world. It precisely protects your data before it even transmits to the destination by encrypting it right after generation. In this way, it even hides everything from the internet service provider, which, in this case, is the public WiFi network.
So, you see, when your data gets encrypted, nobody, including the hackers, can see your online activities.
Therefore, while a VPN is an added facility to evade almost all sorts of web tracking, it is a requisite for using public WiFi securely.
Whether you’re a frequent traveller or a person at home, having a VPN is something that we always advise. It isn’t even costly to fit into your monthly budget if you choose a VPN wisely. So, ideally, you should have it turned on all the time. But, whenever you need to use free WiFi at some public place, you must remember to turn it on even before you connect to the WiFi.
You can take a look at this list of the best VPNs to decide which VPN you should use.
Enable 2FA on your accounts
If you can’t use a VPN or need to do something for which you need to turn your VPN off, then password security is the next thing you should take care of while connecting to public WiFi.
That’s because your passwords would be clearly visible to the hackers present over the network. Even if you ensure HTTPS-only browsing, password security is always risky.
Therefore, you should enable two-factor authentication on your accounts. This will at least protect your accounts from being lost at the hands of hackers if you lose your password to them.
Then, right after your session completes and you disconnect from the public WiFi, make sure to change your passwords the next time you sign in. This will further eliminate any risk to your accounts due to password exposure.
Avoid financial transactions
While public WiFis are a big no-no, they’re even more dangerous for sensitive online activities due to the reasons mentioned above.
For instance, if you’re on public WiFi, you can perform routine searching for your queries. But avoid doing any financial transactions on these networks. This is especially important given that you can’t access your online banking account with a VPN. Likewise, you may also face trouble signing in to your social media accounts via a VPN, as the service would consider it a malicious login attempt due to a change of location.
So, you should simply rule out signing in to any crucial service while using WiFis in a public place. In case of any urgency, your mobile data is always there to help. Again, it’s better to spend a few bucks than lose your identity or your money to criminals.
Monitor your Bluetooth connectivity
Public Wi-Fi can be a vulnerable access point for cybercriminals to steal your data and identity through Bluetooth connections.
Blue-bugging and bluesnarfing are hacking techniques that can give access to your mobile device and its data. Also, blackjacking involves searching for discoverable devices on public Wi-Fi and sending spam as a text message or email.
Protect yourself by avoiding public Wi-Fi, securing your Bluetooth connection, and being cautious of suspicious messages or emails.
Turn off file-sharing and close shared files on your computer
When connecting to public Wi-Fi, be careful sharing folders as they can be viewed by anyone on the network.
Close them and turn off file-sharing before logging in. Additionally, you can adjust your privacy settings to ensure they are different for public and private networks.
Change your device settings
Some easy modifications to your devices can significantly reduce their vulnerability to attacks. Below are some of the tweaks you can make;
- Update your operating system: Keeping your devices up-to-date is crucial as most software updates are automatic and contain security patches that protect against known vulnerabilities. Avoid downloading software updates over public Wi-Fi as fake updates can be triggered, and instead, check for updates on a secure and private connection.
- Turn on the firewall: A firewall monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and uses predefined security rules to either allow or block the traffic. Its purpose is to prevent unauthorized or malicious access to your device. Most computers now have a built-in firewall, and it’s important to ensure that it’s turned on.
Follow these steps to enable the firewall on a Mac,
- Go to System Preferences
- Select Security & Privacy
- Choose the Firewall tab
- Unlock the window, and click Turn On Firewall.
To turn on the firewall on Windows, you can follow these steps:
- From the Start menu and go to Settings.
- Select ‘Security & Privacy.’
- Choose ‘Update & Security.’
- Click on ‘Windows Security’ and select ‘Firewall & Network Protection.’
- Check if the firewall is on. If not, turn it on.
- Disable automatic Wi-FiWiFi connection: Disabling automatic connections is one of the first steps to making your devices less vulnerable to attacks. To turn off this feature on Windows, follow these steps;
- Go to the Settings menu
- Click on Network & Internet, and then Wi-FiWiFi.
- Next, select Manage Known Networks.
- Right-click on any network you don’t want to connect to automatically.
- Finally, select ‘Properties’ and uncheck the option that says ‘Connect Automatically When in Range.’
To disable automatic Wi-FiWiFi connections on a Mac, follow these steps:
- Go to the System Preferences menu.
- Click on “Network.”
- Choose the network you do not want to connect to automatically from the list on the left side of the screen.
- Uncheck the box next to “Automatically join this network.”
- Click on “Apply.”
To disable automatic Wi-FiWiFi connections on an iPhone, follow these steps:
- Go to the Settings app.
- Tap on “Wi-FiWiFi.”
- Choose the network you do not want to connect to automatically.
- Toggle the switch for “Auto-Join” to the off position.
Managing system security and maintenance

The next thing we really want to emphasize through this security guide is system updates and maintenance.
No, you don’t need a hardware toolkit for this. Nor do you need an engineering degree.
What you need is a sharp observation and knowledge of the apps and the system you use.
The main reason behind the success of most cyber attacks is a lack of system security and maintenance. Either the average internet user doesn’t know how to protect their respective device (whether computer or app). Or, people do know about it but pay no attention to securing their systems.
It means if you stay vigilant in ensuring your device’s security and maintenance, you won’t likely become a victim of any cyber threat. Just do the following.
Keep your device and apps updated
Although, installing the latest updates, especially the huge ones, looks eerie. You often ignore downloading the updates only because you aren’t comfortable with the updates occupying so much space on your device.
But, technically, this is a very wrong and dangerous approach. That’s because these updates not only bring new features but, most of the time, they carry important security fixes. These are the bugs that criminal hackers search for to target vulnerable users. So, while the company can fix the bug and release the patch, if you don’t update it, then only you will be responsible for any cybersecurity mishap.
Installing updates isn’t only important for apps or software but also for the operating system. In the latter case, the updates may also save you from potential exploitation due to weak hardware.
It isn’t difficult to install the updates. On your smartphones, it is even easier as the updates, whether of apps or the firmware, will reach you automatically. Then you just have to allow the updates to install when prompted.
In the case of your desktops/laptops, here’s how you should proceed.
For Windows machines:
On Windows 8:
- Open the “Start” menu. Then click on the “↓” button towards the bottom. Now go to the PC Settings menu and select “Update and recovery.”
- Under the “Windows update” tab, click on “Choose how updates get installed.”
- Select the option “Install updates automatically (recommended)” from the dropdown menu. Check the options for “Recommended updates” and “Microsoft Update” and click on the “Apply” button.
On Windows 10:
- Go to Settings > Updates & Security > Windows Update > Advanced options.
- Turn on the “Receive updates for other Microsoft products when you update Windows” option.
For macOS/OSX:
From the main menu, go to System Preferences > App Store > Automatically check for updates. Check all the options belonging to this menu.
For Linux:
Depending on the desktop environment, we can’t give a step-by-step guide here. But you’ll most likely find these settings under the main menu and then system settings.
Activate system firewall

Just like a wall protects you from external threats, a system firewall saves your device from cyber threats.
Some people confuse firewalls with antivirus. In reality, the two are different in the way they tackle things.
Firewalls specifically aim at repelling any external access to your system with a preventive approach. That is, it repels the incoming threats over the internet before infection. At the same time, an antivirus works after the infection happens to remove the threat.
The two may also couple, or a single tool may work in a two-way to adopt both preventive and defensive approaches. In this way, the security program not only repels the threats before infection but also removes the threat after infection.
Apart from malicious threats, firewalls can also help you stop unnecessary or unsolicited access to your device from the users present on your network. As you limit user access to your system, you also minimize the chances of potential infection from a vulnerable system accessing your device.
If you’re wondering which firewalls you should set up on your systems, check out this list of the best free firewall software. You’ll also find more details about firewalls in the same security guide.
Whereas, if you wish to go the manual way, here’s how to set up the firewall on different systems.
On Windows:
Windows users don’t have to worry much about system security as Windows comes with “Microsoft Defender” (previously known as Microsoft Security Essentials) as a built-in tool. Also, Microsoft ships the system with a “Windows Firewall” that works together with the antivirus.
So, you can simply use these tools as an initial security measure for your device.
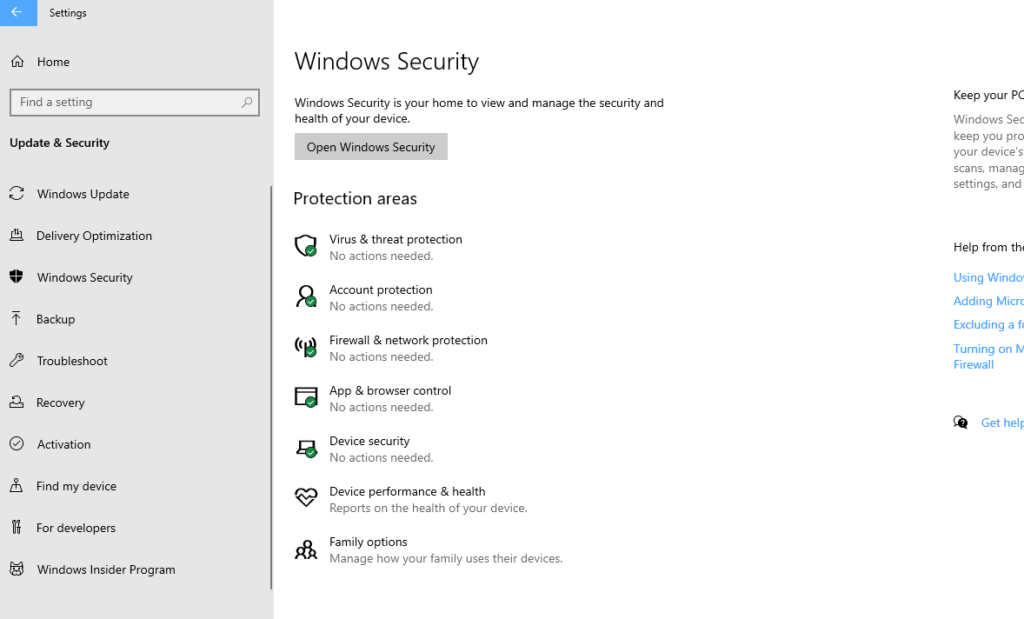
To activate Windows Security, go to All Settings > Windows Security. Then turn on all options (as shown in the following picture).
Follow this path to activate system security for users having versions earlier than Windows 10.
Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Defender Firewall > Customize Settings. You should now turn on all the options to activate the Firewall security.
On macOS:
Like Windows, macOS also comes with a built-in firewall to protect your device.
To activate it, go to the Apple menu > System Preferences > Security & Privacy > Firewall. Make sure the Firewall status is “On.”
On Linux systems:
Again, the precise settings may vary depending on the distribution, it isn’t difficult to activate it though.
Fortunately, Ubuntu and Kubuntu distros now come with a dedicated firewall, the “Ultimate Firewall”. Users with the latest versions can find it easily in their systems by default.
However, in case you can’t find it, you can install it by running the command “sudo apt-get install ufw gufw” in a terminal window.
After the installation completes, you can then configure it.
On Ubuntu: Look up the firewall and then enable the settings to activate the firewall. In general, you can ‘Deny’ the ‘Incoming’ option and ‘Allow’ the ‘Outgoing’ one. This will prevent any threats from coming to your device from the internet.
On Kubuntu: go to Applications > Settings > An easy way to configure your firewall.
Apart from Ultimate Firewall, you can also install other firewall apps on your Linux device, such as ClamAV (run the command “sudo apt-get install clamav clamtk”). You can then configure it on your device in a similar way.
Back up your data
Apart from securing the hardware and software of your device, there is one more thing that needs your attention – your own data.
In fact, your data is the most vulnerable thing when it comes to computer internet security. That’s because any loss of your personal data can have potentially long-term consequences for you, including identity theft.
Plus, malware infections may also damage or corrupt your important files, thus making you lose sensitive information.
However, you can minimize all these risks with just one thing – backup maintenance!
Of course, you might have maintained your data backup at your workplace. Sometimes, this process may be automated, and you don’t even notice it as it runs in the background.
But backing up data isn’t just a corporate practice. Rather it’s a basic computer security practice to protect your personal data too.
So, even at home, with your laptops or smartphones, you should always remember to back up your files in a safe place.
Earlier, people used to store data to flash drives. Today, thanks to technology you can even connect separate storage drives with huge spaces to our systems to backup data. In this way, you won’t even lose a single important file if your system security fails against a malware attack at any time.
While maintaining backups in hard drives is more secure, it also adds maintenance costs to the user. If you don’t have enough space at home to safely store these drives, you might risk your data if the drive gets damaged.
Plus, hard drives also compromise data accessibility and portability.
So, you can alternatively go for cloud storage services to store your data. This is just another strategy to maintain a copy of your data at a place other than your system. It’s also fast, convenient, and accessible from everywhere.
For personal use, you can go for any free service. Google Drive and iCloud are already there for you. You can also take a look at the best free cloud storage services in this article to find the one that best fits your needs.
Whereas, for corporate or business use, you can try paid backup services to secure data. You can even opt for the ones that offer automatic backup maintenance upon scheduling. This will save you from the hassle of remembering when to back up your data.
The more dedicated services also let you choose what data to back up and what to ignore. Hence, they save your space from being filled up with unnecessary files.
Responsible use of social media

You might wonder what’s there to be responsible for on social media, right?
Well, you aren’t wrong if you think that way because social media is all about fun.
Certainly, it’s fun to share your precious moments as well as your routine activities with your kith and kin.
But your sweet postings are what the hackers hunt for. That’s because these posts reveal too many details about you – even more than what you share.
For example, when you post about your recent trip to somewhere, say, from the US to Greece, on Facebook, and you tag your friends and close relatives, what would happen next? The ones you tagged would engage with your post, commenting on their best wishes, right?
While this looks innocent, for an adversary, it’s a treasure trove.
A third person would now not only know about what you’ve shared on your profile, including your name, picture, and location but also about whom you’re linked with – your family, distant relatives, friends, etc. They would also know your financial status if you describe somewhere why you’re traveling- like, for business or vacation.
Plus, they can even follow you through as you travel and post about your stopovers on your timeline.
This is what an average stranger would know about you. If the adversary knows a bit of technicality, then the extent of data the attacker would collect about you is unimaginable.
This is all in addition to what the service itself collects about you. If it’s free, like Facebook, you should know that your data will now land in the hands of attackers sooner or later.
Particularly, Facebook is one of the most intrusive social media platforms that has admitted that it monetizes data. The service has now even treated WhatsApp to collect your data and share it with other Facebook products.
So, while the platform is fun, you should never use it so aggressively to compromise your personal life. We have already talked about maintaining privacy on Facebook in this article in detail. Perhaps, you should read it again and start applying all the tips you can to protect your privacy.
Besides Facebook, other social media platforms, especially the free ones, also collect your information. They might not be as aggressive as Facebook, but still, they collect enough information about you that makes your data worth selling to advertisers.
Therefore, you should always keep your privacy on top priority by applying social media security best practices. Avoid sharing your pictures, biodata, location details, family history, and other personal stuff that you don’t like to share with any stranger in real life.
What you should not share
Everything you write on Facebook may become public at some point, whether it’s a new post or a comment on someone else’s post or photo. You have limited control over the privacy of your comments on other people’s content.
While you have more control over your own posts, Facebook is known for making unannounced changes to privacy settings, so it’s safest to assume that nothing is truly private.
How to implement basic privacy on Facebook
You can access Facebook through its official website or official applications for different platforms. While there are many options, the website is the main Facebook version as it has the most comprehensive privacy settings available.
To set up your privacy, click on the lock icon at the top-right of the Facebook page. This icon contains the main categories of privacy options that you can select from to customize your privacy settings.
The Privacy Checkup is a useful tool to configure how your information is shared on Facebook. It guides you through a step-by-step process to ensure that your information is not set to Public and is only shared with Friends, who are the people you’ve accepted as friends on Facebook.
The next page after the Privacy Checkup shows any apps’ permissions to your Facebook account. This includes websites and mobile apps you’ve logged in to using your Facebook username and password. This article recommends choosing the “Only me” option for these apps unless you specifically want them to make posts on your behalf. This ensures that any potential posts these apps make are only visible to you.
Keeping conversations safe

Just like you need to be careful while using social media, you should protect your personal and business conversations as well.
That’s because you often share your most sensitive details with others during conversations. From your identity numbers to your banking details, you often share all this data with others via emails or messages over various apps like WhatsApp.
While this has made data sharing way more convenient, it’s also a security risk. Anyone intercepting your network or communication medium can easily access all this sensitive data.
Of course, you can’t avoid using these media for conversations. But you can certainly protect yourself from third-party intrusions.
Here’s what to keep in mind.
Protect your emails
Emails are the most used means of communication for both personal and formal purposes. Particularly, the latter is what you should take care of because formal communications often involve sensitive details.
For example, you might email your bank seeking assistance with the account statement. You must share your account details in the message for the bank to assist you. If an adversary reads those details, you’ll be in trouble.
Likewise, your official communications also frequently include worthy data that a perpetrator might misuse.
So, make sure to keep your emails safe by following safety best practices. Avoid falling prey to phishing emails. Whereas, to protect your information, you may also wish to encrypt your emails even when using regular services like Gmail.
Besides, if you’re an avid privacy seeker wanting to secure your emails from being tracked by the service provider, then you can try using a secure email service like ProtonMail or Tuta.
To get more choices, take a look at this list of the best secure email services you can use for personal and business communications. Using these services isn’t so difficult either, and in most cases, you won’t even have to pay to use them. Though, subscribing to premium packages might bring more benefits to you.
Use safe IM apps
Besides emails, you should also focus on keeping your personal chats secure and private. (Though, we believe we won’t have to explain this in much detail as most of you would already know the importance of secure personal chats.)
While SMS used to be a great service for instant messaging, it didn’t help people communicate abroad.
That’s why services like Yahoo Messenger and MSN Messenger gained popularity in letting people connect globally via the internet. However, those services weren’t secure enough for the users.
Thus, people started to look for other apps that bring privacy and security. Nonetheless, the most fun-filled services, like Facebook, aren’t good for instant messaging as they do not respect your privacy the way you deserve.
Likewise, services like Skype or Google Hangouts also failed at providing adequate security to your chats.
Hence, WhatsApp started to gain traction as it boasted end-to-end encryption for all. During the past few years, WhatsApp seamlessly replaced almost all messaging platforms owing to its security and ease of convenience.
However, after the recent update, people are worried about protecting their privacy during regular conversations.
Thankfully, around the same time when WhatsApp emerged, numerous other apps also surfaced online that provide the same or better security to users, without compromising their ability to connect users globally.
Therefore, you can use these apps to secure your personal conversations from hackers, snoopers, web trackers, advertisers, and even service providers.
While the options are many to choose from, you can take a look at this list of the best secure messaging apps that we have compiled for you.
Use secure messaging applications
Messaging apps that use encryption help to protect your privacy and prevent eavesdropping on your private chats. Some of these apps are maintained by large corporations, while others are run by startups.
These apps use end-to-end cipher technology, which ensures that only the sender and recipient can access the message content. Apple’s iMessage also encrypts its messages using end-to-end technology, but its Messages app handles both encrypted and unencrypted messages, which can confuse. Therefore, it’s recommended to use one of the best-encrypted messaging applications to ensure all chats are secure.
The best secure messaging app should have the following:
- Supportive to Multi-platform: A good messaging platform supports multi-platform usage, enabling users to synchronize their messages across different platforms, such as mobile or web apps. Users can also choose to store their private messages in their preferred location and delete them from other locations if they feel uncomfortable. This feature significantly enhances data privacy and security.
- Multi-mode communication: If you’re tired of communicating solely through text messages, you may be interested in using a platform that offers video and audio call APIs. Platforms that offer multiple modes of communication usually allow users to delete messages, which can improve security.
- End-to-end encryption: Secure messaging using end-to-end encryption provides complete encryption of all data transmitted during communication. This means that from the moment a message is typed to when it reaches the receiver, no one, including government organizations, internet service providers, or app makers, can view the data, ensuring maximum security.
Dealing with identity theft

Identity theft is literally what the term suggests – the theft of your identity.
Wondering why we mention an apparently uncommon thing like this in this security guide. That’s because identity theft is the biggest threat you face when you come online.
From social media to web tracking, the data you leave behind (or your digital fingerprints) reveals quite a bulk of information about you. If someone maps all this information, the adversary can easily impersonate you.
As a result, you may face serious issues, from regular scams to financial frauds and even the loss of your bank accounts.
It means you shouldn’t take this lightly, rather, you should remain wary of any baits that make you fall for identity theft.
How to identify identity theft
If you frequently monitor your credit report, you can easily detect any unusual activities going on with your name. So, keep an eye on it and look out for any accounts opened with your name that you can’t recall. If you find anything unusual, you should suspect identity theft.
Besides, after someone steals your identity and performs transactions with your name, soon, you’ll be contacted by all the creditors for reimbursements. This is another clear sign of successful identity theft and exploitation.
Likewise, witnessing any other unusual activities associated with your name also shows that someone is impersonating you.
How to deal with identity theft
Preventing identity theft completely is difficult, and monitoring services only notify you after the fact. However, there are 11 steps you can take to prevent identity thieves from stealing your information:
- Monitor financial and medical statements: Reviewing your financial and medical statements regularly can help you spot fraudulent transactions or charges. When you notice anything suspicious, report it to your bank or healthcare provider right away.
- Always check your credit reports: Checking your credit reports for errors or signs of fraud can help you catch identity theft early. Get a free credit report from the major credit bureaus at least once a year.
- Keep your mobile devices safe: Mobile devices are a prime target for thieves, so protecting them is important. Use a strong password or biometric authentication to secure your device, and avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for sensitive transactions.
- Use a digital wallet: Digital wallets are a more secure way to pay for goods and services. When you use a digital wallet, your payment information is encrypted and stored securely, reducing identity theft risk.
- Shred important documents: Shredding documents that contain personal information can help prevent identity theft. This includes bank and credit card statements, preapproved credit offers, and other sensitive documents.
- Secure your mailbox: Thieves may steal mail to access personal information, so it’s important to keep an eye on your mailbox. Consider using a lockable mailbox, and sign up for USPS Informed Delivery to track your mail online.
- Use alerts: Setting up account alerts can help you spot unauthorized transactions or other suspicious activity on your accounts. Many financial institutions offer text or email alerts for free, so take advantage of this feature.
- Use strong passwords and add an authentication step: Strong passwords and 2-factor authentication add another layer of security to your accounts. Use a complex and unique password for each account, and consider using a password manager to keep track of them.
- Beware of Phishing: Phishing is designed to deceive you into revealing personal information or downloading malware. Be wary of unsolicited phone calls, emails, or text messages, and don’t click on download attachments or links unless you’re certain they’re safe.
- Keep your social security number safe: Your Social Security number is the gateway to your identity, so it’s important to protect it. Avoid always carrying your Social Security card with you, and don’t give out your number unless you absolutely have to.
- Freeze your credit: Freezing your credit reports prevents thieves from creating fraudulent accounts in your name, and it’s free to do. Remember that you’ll need to temporarily lift the freeze if you want to apply for new credit or services that require a credit check.
Got your account hacked? Let’s deal with it
Even after applying all security measures, it isn’t uncommon for average internet users to get their accounts hacked.
Hacking doesn’t mean that someone would change the theme of your hacked account or that it will start posting things automatically. What it simply means is that someone has gained access to your account without consent.
Then, if the attacker has some target, he will most likely lock you out of your account. But if the attacker wants to collect your information, then he may remain silent and would let you use your account normally.
So, identifying a hacked account depends on what the hackers aim at. However, if you vigilantly monitor your account’s behavior, you might sense unauthorized access to it. Here’s what you can observe,
- Check for any emails prompting you about unauthorized login attempts.
- Review your account settings and look for the integration of any unidentified email address or phone number into it.
- Review your profile settings and look for any unidentified changes.
- Check if your account continues to run even after you sign out.
- If you suspect social media hacking and you’ve shared your personal or financial details there, communicate with your bank immediately to detect any unusual transactions. Likewise, perform all the steps we advised above to check for possible identity theft.
If you believe your account is or was hacked, you should also contact the service’s customer support. Discuss the entire matter with them in detail. They might also confirm or rule out your suspicion besides helping you take your account back in control.
Once you’re done with all this, change your account password and apply 2FA to protect your account.
If you suspect damages, it’s better to contact law enforcement authorities and report the matter.
Ensuring business security
Did you think this detailed security guide is meant only for individual users?
Well, although we have mainly discussed all those security tips that protect individual users. Yet, we believe that individuals make up the organizations, and hence, training people at an individual level is essential to protect the organizations as a whole.
And that’s what we expect the business community to focus on, too – cybersecurity training of individual employees.
Train them about how they should protect the passwords of official accounts. Teach them how to keep their workstations secured from external access. Make them aware of the threats arising from phishing emails. The more they know, the safer your company will remain.
Nonetheless, corporate security isn’t about training individuals. Rather, there’s more to do for the management team.
This includes setting up a skilled IT department, including knowledgeable people from the infosec community, as well as developing an overall infrastructure that resists cyber attacks.
While this may sound costly, it’s better to spend on your security initially than to suffer far huger losses after an unfortunate incident. There already are numerous tragic stories from the corporate world where companies even had to shut down post-cyberattacks. You should do everything to not become one more of such tragic stories.
So, keep your company network safe from external access by fixing any bugs promptly, keep all the software your business uses up to date, set up a secured company website with SSL, develop a resilient infrastructure, and protect it with a robust firewall to prevent threats like DDoS, and, final, join hands with a cybersecurity firm to assist you in keeping your company safe from all threats.




