VPNs and proxies both serve to change online locations and access restricted or foreign content. However, comparing a VPN and proxy shows that the two tools are not a substitute for one another. Instead, they are meant to serve different purposes.
While proxies focus more on IP spoofing and content unblocking without compromising speeds, VPNs are intended to protect users’ online privacy despite minor speed lags. Therefore, knowing the pros and cons of VPNs and proxies is vital to making the right choice.
This article compares proxy and VPN head-to-head and explores which one serves better.
What is a VPN?
VPN is an abbreviation for the term Virtual Private Network. The purpose of a VPN service is to provide you with complete security and anonymity when browsing cyberspace.
When you use a VPN, all your data is encrypted. The service masks your IP (internet protocol) address by channeling all your information via a tunnel within a remote server. For example, you could be surfing in Canada with your IP address showing the USA; hence, your geo-location remains hidden at any time.
VPN is for anyone who wishes to redirect their internet traffic history and make it untraceable.
Through encryption, you secure your data from being accessed by cybercriminals. Also, you remain undercover from the eyes of the government. So, if anyone tries to snoop on you, your data will appear as nothing but a bunch of incoherent random characters.
How does a VPN Work?

A VPN can hide your IP address, web browsing history, and device.
How this service does this is relatively simple.
VPNs channel your web traffic through a tunnel while encrypting the data as it passes through. At the end of the tunnel is the exit “gate” opening to a new location. That’s where your data reaches the internet.
In other words, all your internet activity passes through a secret channel rather than your ISP.
Therefore, when you browse the internet, your data seems to come from an unknown source (VPN) rather than your device.
Pros and cons of using a VPN
Pros:
- It lets you access geo-restricted websites safely.
- Keeps browsing activities private from online snoopers.
- It helps evade content censorship.
- Protects IP address and online location.
- Minimizes the risks of potential data breaches and hacking attacks.
Cons:
- Affects browsing speed.
- Free VPNs are not reliable for privacy.
- Inadequate IP leak protection may expose your identity online.
Why use a VPN?
There are many reasons why one might use a Virtual Private Network VPN. Some common reasons VPNs have become so popular include the following.
Protecting vulnerable data
Your personal information, such as your bank details, passwords, and private messages, is always at risk of being accessed and taken advantage of by cybercriminals.
All these criminals need to view your data is a link, email, or unsolicited cookie. VPNs employ the AES encryption algorithm to encrypt all information that passes through your network.
Accessing geo-restricted content
Unsurprisingly, much of the viewable content to others may be restricted for viewing to you. Many popular streaming websites like Netflix, Dinsey+, and Hulu limit who can view their content based on where they are.
You would have encountered the same problem when viewing specific Youtube videos where a message reads, “This video is unavailable in your country.” It often happens for complying with local law or the creator’s choice of not making their content available.
Nonetheless, overcoming geo-restriction is easy. You can use a VPN client to mask your IP address and connect to a server where the content is available for viewership.
Increasing network speed
Using a VPN generally reduces your network’s connectivity speed due to the extra work of encrypting and decrypting the data.
But did you know using a Virtual Private Network VPN under certain circumstances can also improve your speed? You will understand how VPNs can increase speed if you have heard of ISP throttling.
ISP (Internet service provider) throttling, or bandwidth throttling, is the intentional slowing down of your network speed by your service provider.
Why? I hear you ask.
It is only because your service provider limits how much high-speed data is available to you. Once you hit the data cap, you will notice the slow speed.
What is a proxy?
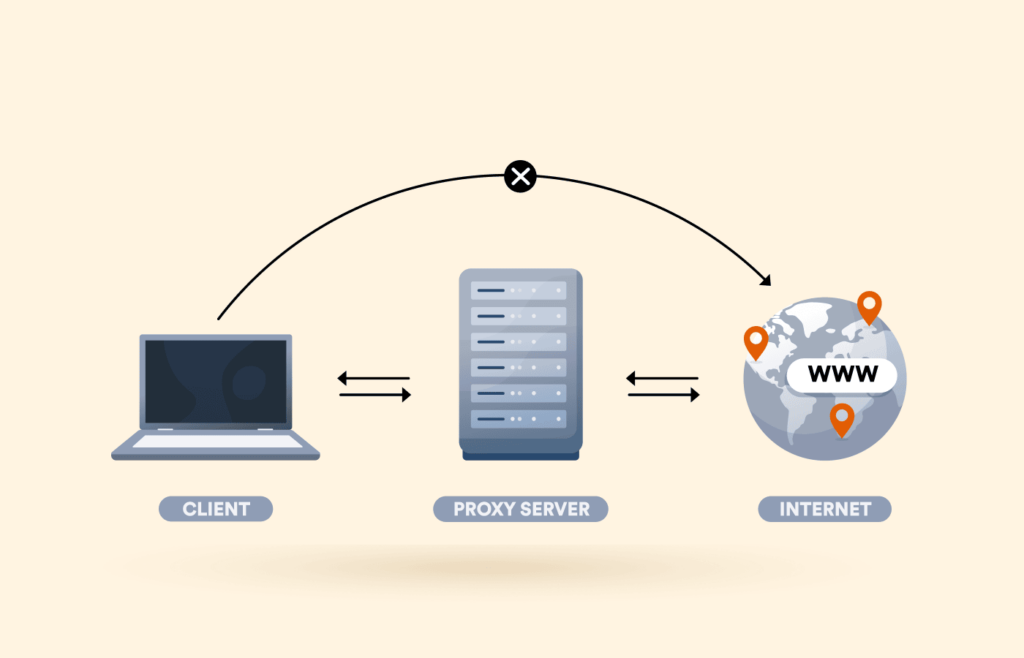
A proxy server is an independent and secure server through which all your data passes. Essentially, a proxy acts like a gate that opens and closes to let information pass through.
The privacy and security provided by a proxy will depend on your needs. First, a proxy server will accept your request to access a webpage and then allow entry to it and vice versa.
Proxy servers add a security system to your internet usage, practically working as a firewall, a medium for shared connection, and a webpage filter.
Pros and cons of using a proxy
Pros:
- Easy to install and use.
- Usually available for free.
- Allows changing online location.
- Offers access to content from abroad.
- It helps implement unauthorized access to some websites.
Cons:
- Fails at evading strict geo-restrictions on some platforms.
- This may cause compatibility issues with the local server network.
- Usually logs data, risking a data breach.
- It does not support use on more than one device.
How does a proxy server work?
As you know, every network has a unique IP address. The proxy server masks this IP address and act as a medium to channel requests on your behalf.
In doing so, all your data gets encrypted, giving the impression of appearing from a different location altogether.
It is important to note that, unlike VPNs activated in the background, you can only use a proxy site through a proxy server.
However, a proxy only provides superficial anonymity. To take complete charge of masking your location and identity, VPNs make a better choice.
The different types of proxies
Here are the common types of proxy servers.
Transparent proxy
A transparent proxy gives you the experience you would get on your home computer. However, it can be forced and connected without your consent.
These proxies are ideal for companies that don’t want their employees to know they are using proxies. This gives businesses the advantage of a seamless user experience. Unfortunately, transparent proxies are vulnerable to security threats like SYN-flood denial-of-service attacks.
Forward proxy
A forward proxy facilitates data transmission to specific users within an internal network. The proxy examines incoming requests to determine if it should establish a proxy connection.
Forward proxies are ideal for internal networks requiring a single entry point. It protects the IP addresses in the network and facilitates seamless administrative control. Regrettably, a forward proxy can restrict an organization’s capacity to address the needs of individual end-users.
Anonymous proxy
An anonymous proxy will make your internet activity invisible. It works by accessing the internet on your behalf while concealing your identity and computer data.
Anonymous proxies are best suited for those who want complete anonymity online. However, they are suspicious, and you can sometimes face discrimination or pushback when accessing some websites or services online.
Distorting proxy
A distorting proxy reveals its status to a website but conceals its identity by manipulating its IP address.
This is a good way to hide your location when accessing the internet. It will make you seem like you are browsing from a different country and give you the advantage of hiding your identity and proxy status. So, your identity will still be secure even if your proxy is tracked. Unfortunately, some websites block distorting proxies, which could prevent you from accessing the sites you want.
High anonymity proxy
A high anonymity elevates your privacy by erasing your data before connecting to the target site. It is best suited for users who require absolute anonymity, like employees who don’t want their employers to trace their online activities. However, some high anonymity proxies are decoys set up to collect user information.
Residential proxy
A residential proxy assigns you an IP address of a physical device where all your requests are routed through it. This proxy will enable you to block suspicious or unwanted advertisements from competitors or malicious actors.
While residential proxies are more reliable and trustworthy, they are costly. So, determine if the benefits justify the additional expense.
Datacenter proxy
A data center proxy is provided by a third-party company instead of your internet service provider (ISP). The proxy server is hosted in a physical data center, and your requests will be directed through it.
This is a great option if you want an inexpensive solution and quick response time. For example, you can use it to promptly gather information on an organization or person. They have the advantage of giving you the power to harvest data quickly and inexpensively. However, they have weak anonymity, which might expose your information or put your identity at risk.
Secure sockets layer (SSL) proxy
An SSL proxy decrypts the connection between the client and the server. Since the proxy encrypts the data in both directions, it is invisible to the client and the server.
These proxies are most effective for companies requiring advanced protection against vulnerabilities the SSL protocol identifies and mitigates. Since Google prefers servers with SSL, an SSL server can help improve your website’s search engine ranking.
Shared proxy
Many users use a shared proxy at once. The provider will assign you a shared IP address, allowing you to access the internet while seeming to be in a different location.
Although a shared proxy might be affordable, it has a slow connection because of the multiple users. Moreover, a site might ban you because of someone else’s mistake.
Public proxy
A public proxy is free and accessible to anyone. You will still get an IP address to conceal your identity from the sites you visit. It is a good choice if you are on a budget and speed and security aren’t major concerns. On the downside, public proxies are slow because of the many free users. Also, you risk exposing your information to others on the internet.
When to use a proxy?
Although proxies aren’t as secure as VPNs, they remain in trend. That’s because using these tools has its benefits.
You may want to use a proxy for the following purposes.
Spoofing public IP address
Proxies serve as a quick means to mask your IP address. Whether you wish to hide your real IP for privacy or want to get rid of online tracking, you can quickly use a proxy to change your IP without going through technical settings.
Access content from another location
Like VPNs, proxies also help you access content from another region.
Although, a web proxy isn’t robust enough to bypass geo-blocking. So, you might face trouble accessing blocked content. However, for other quick activities, proxies work great. For example, if you are abroad and want to know the local news from your homeland, you can use a proxy to change your online location.
Change location free of cost
Most proxy services, particularly the ones meant for individual use, are free of cost. Even if they don’t offer hundreds of locations for free, you can still get at least 4 to 5 different locations. Therefore, a web proxy is your best bet if you temporarily need a free tool to mask your IP.
Difference between proxies and VPNs
Although both are used to access geo-restricted content and mask user identity, the difference between a proxy and a VPN client is substantial. Knowing which one to use would require weighing each advantage and disadvantage. So, here is a quick comparison of VPN and proxy, considering different parameters.
| Feature | Proxy | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free (Although some are paid) | Paid (Although some are free) |
| Number of users | 1 | Depends on the service (Some support unlimited simultaneous devices) |
| Encrypt web activity | No | Yes |
| Encrypt IP address | No | Yes |
| Coverage | 1 app or website | All apps and websites |
| Sells user data | Yes | Most premium services don’t, but some free services do |
| Slow down browsing speed | Yes | Yes |
| Can bypass geo-restrictions | Yes | Yes |
| Compatible with gaming and streaming | Yes | Yes |
Encryption
VPNs are famous for their ability to mask IP addresses and encrypt all data that passes through your network. However, proxies do not encrypt any data, leaving your information vulnerable to cybercriminals and allowing the government to track your internet activity.
No-log policy
It is essential to know the “No-log policy,” which some, but not all, VPN services implement.
The no-log policy guarantees that VPN providers will keep no track of any information accessed through a VPN. When (for example) the government requires a Virtual Private Network VPN provider to hand over user activity logs, a no-log VPN cannot share the data. A proxy server provides no such guarantee.
Free VPNs vs. proxies
There are several free VPNs and proxies in the market, but there is a catch. These free services do not provide the same protection and features as their premium counterpart.
Free proxy sites are not only less secure but also incredibly slow. In addition, the ability to make configurations within free proxy servers is also substantially limited.
On the other hand, free VPNs provide a limited list of servers to mask your IP address and do not fully encrypt data as it mostly passes through their channel. Someday, your free VPN provider might also sell your information.
Secure team collaborations
Suppose you are looking for an option to work collaboratively while also remotely and safely, then a proxy server is the right choice.
A proxy acts as a gate to restrict what content the team views and what should remain out of reach. VPNs do not provide this gated restriction. Anyone with access to a VPN client is provided security, but it does not take away any freedom to browse.
Ease of use
Knowing about the importance and uses of proxy and VPN won’t help if you do not understand how to use the tools.
Anyone with basic knowledge of using a PC will find accessing and using a VPN service is a piece of cake. The same, however, cannot be said for proxies. The initial stages of using a proxy are the most technically challenging ones. Yet, once you get used to it, changing locations and configurations becomes pretty easy.
Speed
Using a proxy and a VPN will drop your network speed slightly. You can reduce this drop in speed by connecting to a server close to your location and having fewer people connected. Most of the premium VPNs available today tell the network load on a particular server at a time.
Do note that the speed drop when using a proxy is less when compared to the speed drop when using a VPN because of the underlying encryption the latter applies. However, as mentioned previously, VPNs can also increase speed upon use as it overcomes bandwidth throttling.
Cost
It is no surprise that VPNs cost more than an average proxy server. It is valid for both the running and maintenance costs of both services.
That’s because a VPN offers added security, speed, and the ability to encrypt data between channels. For these reasons, a VPN, under any condition, will cost more than a proxy.
Do you need a proxy if you have a VPN?
No. A premium VPN is much better than a proxy. You could use a proxy to change your IP address, but it won’t encrypt your connection. Also, some proxy services may collect your data. However, a reputable VPN, like NordVPN, employs sufficient security measures to keep you safe and doesn’t collect user data.
VPN or proxy for personal use
For individual users, VPNs offer better security, privacy, and anonymity. In addition, if you live in one of the repressive regions, a VPN may help you gain more liberal access to the internet. However, to run a VPN successfully, you must ensure that it has faster base speeds. Otherwise, your browsing experience will be ruined.
Proxies, on the other hand, offer better speeds. Therefore, it is suitable for those users who merely need to spoof IP locations for the time being to access some content.
Can I use a VPN and proxy together?
Yes, you could use a VPN and proxy together, although the configuration process may be difficult. Also, it is not advisable as the proxy server will add extra load, causing slow speed. So, you should do one or the other. For example, use a VPN to protect your internet and a proxy if you only want to change your IP address.
Proxy vs. VPN for businesses
For businesses, VPNs are great as they ensure security.
However, business activities often do not require security only. Instead, they need fast speeds and better internet freedom, where proxies are crucial. Alongside these benefits, proxies also help employers determine how the staff connects to the internet, as explained above.
Besides, business proxies facilitate companies by providing many valid IP addresses in different locations – something desirable for large businesses.
(Interested in getting a proxy for your firm? Check out this comprehensive list of businesses’ best proxy service providers.)
VPN or Proxy for torrenting

There are two powerful tools to mask your torrenting activity: a VPN and a proxy (SOCKS5).
However, not all VPNs allow torrenting, as it is banned. To check this, VPNs may also employ sneaky data-logging practices. Therefore, choose a VPN with a zero-log policy even if you use the best torrent sites considered safe.
Also, ensure your provider does not cap bandwidth, provides DNS and IP leak protection, and supports torrenting.
On the other hand, proxy SOCKS5 is an excellent torrent proxy (the only available P2P proxy server).
Although, unlike VPNs, proxies do not provide encryption. Also, when using a proxy for torrenting, you must keep configuring your proxy settings to match the torrent client. That gives VPNs an edge, yet it doesn’t diminish the importance of a proxy.
Some of the best torrent clients include;
- uTorrent
- BitTorrent
- QBittorrent
- Vuze
However, some other torrent clients do not support proxy servers. These include;
- Frostwire
- Transmission
Once you have SOCKS5 proxy server login credentials, torrenting becomes relatively simple.
You will get the server’s address, port number, username, and password. After adding your login credentials, move to the configuration/settings tab. Then, change the settings to match the compatible torrenting client. (Most torrent clients have a detailed how-to guide on their torrent website. Feel free to go through it in case of any confusion).
Also, note that a SOCKS5 proxy server differs from a logging proxy. (I advise you never to settle for a logging proxy as these services often use free HTTP proxy that does not mask your IP address, putting your security at risk.)
Proxy vs. VPN for Netflix
If you have been accessing Netflix via a VPN or a proxy server, you would have encountered the error code m7111-5059 at least once. This error code reads,
Whoops, something went wrong—streaming error. You seem to be using an unblocker or proxy. Please turn off any of these services and try again.
That error message appears when Netflix detects the use of a VPN or proxy to view geo-restricted content.
Why does Netflix restrict its content? You may ask here.
It is simply because Netflix has not acquired the necessary rights to stream its service to every region worldwide.
The strictness of banning VPNs and proxies increased in 2016 in an attempt by Netflix to enforce its copyright obligations.
Since then, proxies have almost become useless for unblocking Netflix. Nonetheless, there still exist some robust VPN providers that seamlessly help you resolve the Netflix proxy error.
NordVPN vs. proxy
Proxy servers can indeed mask your IP address. Still, continually configuring your setting to change locations once the proxy error appears is a hassle. That is why I recommend using NordVPN.
NordVPN provides access to ten countries’ Netflix catalogs. At the same time, it allows you to access this content through any server. NordVPN currently has more than 6,800 servers in 113 countries. Anytime the proxy error appears, you can switch to another server.
The VPN is tested to redirect you to Netflix USA (which has the widest variety of content).
Additionally, NordVPN has a zero-log policy; hence you can trust the service for your data security.
As for convenience, it allows ten simultaneous connections on a single account. Plus, it supports Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, Linux, and Amazon Fire TV. That means you can easily use this service to protect all your devices.
FAQs
Not really. Your data remains safe with a VPN while getting all the benefits a proxy offers. So, you’re good if you use a VPN alone.
While you can technically use them together, you don’t need a proxy because you have a good VPN. Recurrently rerouting your data through the proxy and VPN servers will only slow down your internet. Also, you only need them together if your proxy service offers a specific location that your VPN does not.

